Theory
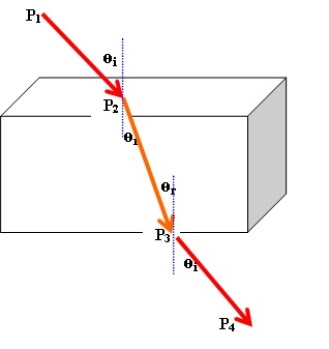
When light rays pass from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, the rays will be deviated from its original path when it enters the other medium. The reason for this deviation is that light travels with different speed in different media. This effect is called refraction. The refractive index (n) for any medium with respect to air is equal to the ratio of the speed of light in air (c ) to the speed of light in the medium(n=c/v).
According to Snell's law the refractive index (n) for a medium relative to air can be related to the angle of incidence (өi) of the rays from air to the angle of refraction of the same ray in the medium (өr).
Snell's law